The pumps have become a most vital part of all household, industrial, and many other applications. They are most widely used all over the world.
There are multiple types of pumps according to the requirements of different applications like gear pump, piston pump, centrifugal pump, reciprocating pump.
The gear pump is the most widely used pump. The name of this pump represents that it uses gears for operation.
In simple words, the gear pump transfers fluid from one place to another by using gears.
These gears use to deliver force to move the water inside the pump. This article gives you an overview of the gear pump. We, therefore, explain to you an overview of the different types, working principle, applications, advantages, and disadvantages of these pumps.
Must read: Piston Pump Explained
What is a Gear Pump?
The gear pump is the most common positive displacement pump (PD). This pump moves the water by using a series of gears.
These gears are named driver gear and driven gear. These gears are meshed with each other. The main objective of the driver gear is to drive the driven gear. This driver gear connects with a shaft.
The shaft gets power from an electric motor or generator and delivers this power to the driver gear.
The gear pump provides a smooth pulsation-free flow which is proportional to the gear speed.
Working of Gear Pump
- Firstly, the power is delivered from the electric motor to the shaft.
- When the shaft rotates, it further transfers its rotation to the driver gear.
- The driver gear further moves the driven gear, which is meshed with the driver.
- Due to the rotation of these gears, a vacuum generates inside the pump due to that water starts to enter the pump. During this process, the inlet valve opens, and the discharge valve remains close.
- As the suction process, the inlet valve also closes, and water is trapped between the gears because there is no direct way for the water to go into the discharge valve.
- After this process, the drive and driven gears move together. With the movement of these gears, the trapped water slowly flows toward the discharge valve.
- In this way, the water is pressurized and delivered up to the desired area.
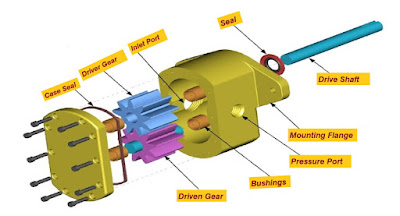 |
| Gear Pump Part |
Different Types of Gear Pumps
- External Gear Pumps
- Internal Gear Pumps
External Gear Pump
It has two gears, the idler or driver gear, and driven gears. The idler gear connects with a shaft. Some gear pumps don't have a shaft.
In such cases, the gear is directly connected with the power source (i.e., electric motor). However, if the pump has a shaft, then the shaft connects with the motor, and one end of this shaft links with the idler or driver gear.
When the gear idler and driven gears leave some space on the suction side, the cavity generates inside the pump.
As the gear continues to rotate alongside the pump housing, fluid enters the cavity and is imprisoned between the teethes of the gears.
This imprisoned fluid can migrate from the duction end to the discharge end in the housing area.
As the area between the teeth of the gears decreases on the discharge side, the fluid area also reduces due to its pressure incases.
Due to the high pressure of the fluid, the pump forces the fluid to be discharged. No fluid can move backward from the discharge side because the gears mesh very tightly.
Due to the close tolerance between the gears and the cover, the pump increases the suction power at the inlet and prevents liquid from escaping from the discharge end.
The external gear pumps have the capability to use herringbone, spur, spur, or helical gears.
Advantages of External Gear Pump
- These have a simple design
- They have the capability to transfer a high amount of fluids.
- They have the capability to manage the pressure (i.e., high, medium, and low) according to the requirements.
Internal Gear Pump
Internal gear pumps work similarly to the external gear pumps, but the gears of the internal gear pump have different sizes. It has a large rotor gear that has teeth on the inward side.
Since the second external gear is mainly installed and connected with the rotor so that the teeth of the gears can connect at one end.
The bushings and pinions can connect with the housing of the pump, which holds the idler gear in its position.
A permanent semicircular divider or spacer seals the gap formed by the eccentric mounting position of the idler gear and acts as a seal between the inlet and outlet openings.
As the gears lose their teeth meshing on the inlet side, the cavity produces on the inlet side. As the gear continues to rotate alongside the pump housing, liquid enters the cavity and is trapped by the gear teeth.
By connecting the teeth to the discharge surface of the pump, you can reduce the volume and use force to push the liquid out. The internal gear pump only uses spur gears.
Gear Pump Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of Gear Pumps
- The gear pumps have simple maintenance.
- These pumps have the capability to handle an extensive range of viscosities.
- This pump has a less sensitive cavity.
- It provides a controllable output.
- These types of pumps have easy construction.
- Advantages of Centrifugal pump over Displacement (Reciprocating) pump
Disadvantages of Gear Pump
- These pumps generate extensive noise.
- They supply pulsating flow.
- The gear pump is not best for abrasive fluids because of its meshing gears.
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Reciprocating Pump
Gear Pump Applications
- The gear pump is used in lube oil, crude oil, diesel oil and pitch applications.
- They are also used to transfer isocyanates, mixed chemicals, acids, plastics, and Sodium silicate.
- The also use to pump sludge, latex, lime, kaolin, black liquor, ink, lye, soap, and paints.
- These pumps use in sugar, fillers, cacao butter, adhesives and resigns applications.
No comments:
Post a Comment