Today our post is about vertical axis wind turbine parts. Vertical axis wind turbine are one whose axis of rotation is vertical with respect to ground. There are many parts of vertical axis wind turbine but we have discus few of them Vertical Axis Wind Turbine Parts
Follow are the vertical axis wind turbine parts
- Guide wire
- Hub
- Rotor
- Blades
- Shaft
- Brake
- Gear
- Generator
- Base
Guide Wire of vertical axis wind turbine
Vertical axis wind turbine normally needs guide wire to keep the rotor shaft in a fixed position and maximized possible mechanical vibration
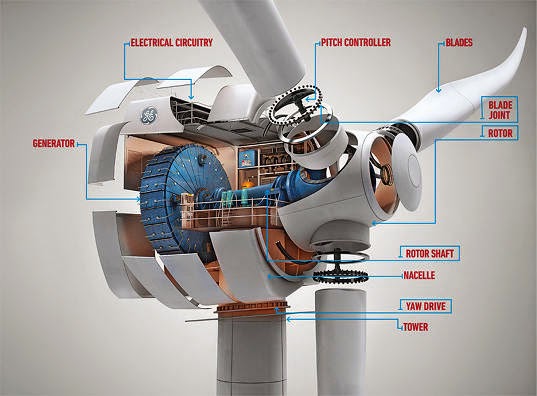
Hub of vertical axis wind turbine
The hub is the center of the rotor to which the rotor blades are attached. Cast iron or cast steel is most often used. In VAWT there are two hibs upper and lower because blades are attached at two points.
Rotor of vertical axis wind turbine
The rotor is the heart of a wind turbine and consists of multiple rotor blades attached to a hub. It is the turbine component responsible for collecting the energy present in the wind and transforming this energy into mechanical motion.
As the overall diameter of the rotor design increases, the amount of energy that the rotor can extract from the wind increases as well. Therefore, turbines are often designed around a certain diameter rotor and the predicted energy that can be drawn from the wind.
Rotor Blades of vertical axis wind turbine
Rotor blades are a crucial and basic part of a wind turbine. They are mainly made of aluminum, fibber glass or carbon fibber because they provide batter strength to weight ratio.
The design of the individual blades also affects the overall design of the rotor.
Rotor blades take the energy out of the wind; they “capture” the wind and convert its kinetic energy into the rotation of the hub. there are two types of blades use in VAWT
- Drage force type blades ( savonius wind turbine)
- Lift force type blades (Darrieus and giromill wind turbine)
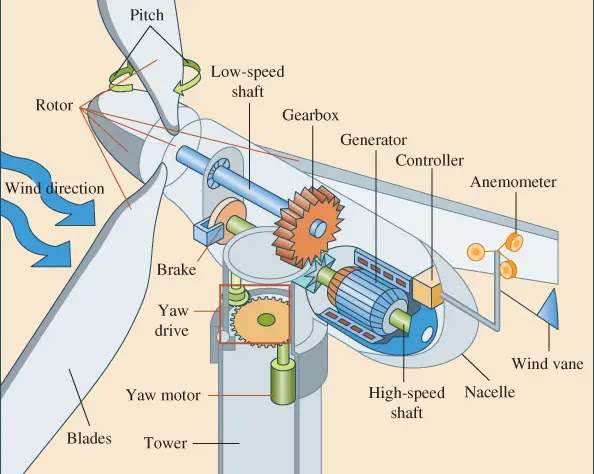
Shaft of vertical axis wind turbine
The shaft is the part that gets turned by the turbine blades. It in turn is connected to the generator within the main housing
Electrical Braking of vertical axis wind turbine
Braking of a small wind turbine can also be done by dumping energy from the generator into a resistor bank, converting the kinetic energy of the turbine rotation into heat.
This method is useful if the kinetic load on the generator is suddenly reduced or is too small to keep the turbine speed within its allowed limit.
Cyclically braking causes the blades to slow down, which increases the stalling effect, reducing the efficiency of the blades. This way, the turbine's rotation can be kept at a safe speed in faster winds while maintaining (nominal) power output.
This method is usually not applied on large grid-connected wind turbines.
Mechanical Braking of vertical axis wind turbine
A mechanical brake is normally placed on the high speed shaft between the gearbox and the generator, but there are some turbine in which the brake is mounted on the low speed shaft between the turbine and gear box
A mechanical drum brake or disk brake is use to stop turbine in emergency situation such as extreme gust events or over speed. This brake is also used to hold the turbine at rest for maintenance as a secondary mean, primarily mean being the rotor lock system.
Such brakes are usually applied only after blade furling and electromagnetic braking have reduced the turbine speed generally 1 or 2 rotor RPM, as the mechanical brakes can create a fire inside the nacelle if used to stop the turbine from full speed.
Also the load on turbine increases if brake is applied on rated RPM. These kind of mechanical brake are driven by hydraulic systems and connected to main control box.
Gear Box of vertical axis wind turbine
The main function of the gear box is to take low rotational speed from shaft and increase it to increase the rotational speed of the generator. Among the types of gear stages are the planetary, helical, parallel shaft, spur and worm types. Two or more gear types may be combined in multiple stages. they are made up of aluminum alloys, stainless steel and cost iron
Generator of vertical axis wind turbine
The conversion of rotational mechanical energy to electrical energy is performed by generator. Different types of generator have been used in wind energy system over the years.
For large, commercial size horizontal-axis wind turbines, the generator is mounted in a nacelle at the top of a tower, behind the hub of the turbine rotor.
Typically wind turbines generate electricity through asynchronous machines that are directly connected with the electricity grid.
Usually the rotational speed of the wind turbine is slower than the equivalent rotation speed of the electrical network - typical rotation speeds for wind generators are 5-20 rpm while a directly connected machine will have an electrical speed between 750-3600 rpm.
Therefore, a gearbox is inserted between the rotor hub and the generator. This also reduces the generator cost and weight
Base of vertical axis wind turbine
Base of VAWT is usually the roof of building on which it is installed.


.jpg)


.jpg)
