One Complete Cycle
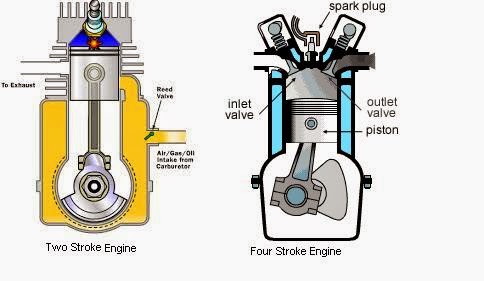
Four stroke internal combustion engine executes four complete strokes within the Cylinder while the crankshaft completes two revolutions for each thermodynamic Cycle while Two stroke engine executes two complete strokes within the cylinder while the crankshaft completes One revolutions for each thermodynamic cycle.Main Strokes
As the mane say fore stroke engine have four strokes Intake Stroke (Induction or Suction Stroke), Compression Stroke, Power Stroke (Combustion Stroke) and Exhaust Stroke while two stroke engine only two stroke First Stroke (Suction & Compression Stroke) and Second Stroke (Power & Exhaust Stroke)
Friction Losses
Because of absence of valve tappets and crank shafts, friction losses are minimum in 2-stroke petrol engine as compared to 4 stroke engine
Power Deliverance
As mention above 2 stroke engine has less friction as compared to 4 stroke engine that's why have more power deliverance an compared to 4 stroke
Rate Of Power Production
In 2-stroke engine, one stroke is working and other is idle stroke and in 4-stroke engines, there is one working stroke and three idle strokes. So the rate of power production for 2-stroke engine is more.
Effects On Environment
In two stroke there is a exhaust of unburnt gasses to the environment so it is harmful to the environment but in four stroke engine there is no exhaust of unburnt gasses to the environment so it is not harmful to the environment
Lose of lubricating oil
As suction & compression stroke take place in a single stroke so there is a heavy combustion of lubricating oil where as in four stroke engine suction and compression stroke are separate so there is no loss of lubrication oil
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)