Timing chain is an integral part of an internal combustion engine ( IC engine). They work to deliver a synchronize rotation motion between engine crank shaft and engine camshaft.
This article is brief introduction of timing chain, what doe timing chain do and how its different from timing belt (timing chain vs timing belt)
To Know about Timing Chain Cost, Replacement read our article on Timing Chain life, Cost and Replacement and To learn about timing chain kit or bad timing belt symptom read our article on What is Timing Chain Kit and Bad Timing Chain Symptoms
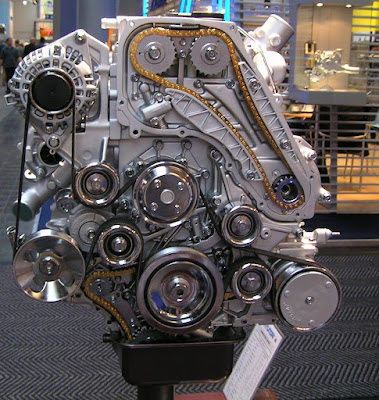 |
| Timing Chain on Internal Combustion Engine |
What is a Timing Chain?
A timing chain is used to connect the crankshaft and camshaft with each other to monitor the engine timing. Engine timing refers to the upward and downward movement of the pistons and opening and closing of the fuel inlet and gasses exhaust valves.
A timing chain is enclosed within the engine and it is lubricated with the engine oil inside the engine.
Both crankshaft and camshaft usually have sprockets attached at their one end and a timing chain is wrapped across the sprockets to connect them with each other.
Types of timing chains
There are different types of timing chains which are categorized according to their design.
The types of timing chains are roller chains, bush chains and toothed chains. Roller chains are further categorized into single roller chain and double roller chain.
Single roller chain is much like a chain of a bicycle whereas double roller chain have dual gears with a chain row on each gear. Roller chains are the most famous and widely used type of timing chains.
Roller chains have higher strength, reduced friction, less wear and give better noise and vibration performance. Double roller chains are more durable, long lasting are ideal for performance applications.
Bush chains are used in heavy and high speed diesel engines whereas toothed chains are not used for heavy duty engines and are also known as silent chains.
There is also a fourth type of timing chain which is a combination of toothed chain and sleeve chain to enhance the power transmission performance of toothed chain.
What Does a Timing Chain Do?
Proper combustion is extremely important for the normal and efficient working of an engine.
Several other factors such as fuel quality, engine temperature and number of power strokes etc. play a vital role in the combustion phenomenon.
But, the timely opening and closing of exhaust and inlet valves are of extreme importance in enriching the combustion quality.
In an internal combustion engine, the power generated during the combustion stroke is received at the crankshaft which runs the camshaft.
The purpose of camshaft is to operate the valves at the suitable rate and this is done by mechanical transmission.
A timing chain serves this purpose and it is an engine’s component that is used to synchronize the motion of camshaft and crankshaft for the proper and timely opening and closing of the engine’s valves.
The valves allow appropriate amount of fuel and exhaust gases to enter and leave the engine’s cylinders respectively to produce the required amount of combustion at a specific speed.
In many vehicles, fuel pump, oil pump and distributor are indirectly being drive by the timing chain. Hence, a sloppy chain can affect the overall performance of the vehicle.
Furthermore, a timing chain also serves the purpose of a damper i.e. it absorbs the vibrations of crankshaft before transmitting the power to camshaft.
Advantages of Timing Chain Over Timing Belt
- Timing chain made of metal will last longer then timing belt as they are made of rubber
- Timing chain offer more strength than timing belt
- They can handle more engine torque and power as compared to timing belt
- Due to their design, timing chain cannot slip and thus offer much higher performance as compared to timing belt
No comments:
Post a Comment