A timing belt is a simplest of machine element designed to transfer motion in an synchronized manner.
This article is about the timing belt working, material, types, applications, advantages, and disadvantages.
Working of Timing belt
Timing belt has teeth on them and these teeth meshes with the teeth of belt pulley. They work much like gears to get a precise rotation motion from their pulley and transfer that precise motion to the next pulley.
Timing belt is design to overcome the slip problem of flat or V belt and deliver power and motion in a precise and synchronized manner.
To know more we recommend you to read our article on Timing Belt , Serpentine Belt & Timing belt Kit
Material of a Timing belt
- Urethane
- Neoprene
- Polyurethane
Applications of Timing Belt (Timing Belt Functions)
Two of the most common applications of timing belts include a stitching machine or sewing machine and an internal combustion engine.In sewing machines or stitching machines, a timing belt is used to deliver power and rotational motion in a synchronized manner.
It delivers power from the machine motor to the machine mechanism. The machine mechanism is designed to convert rotational motion into needle-reciprocating motion.
 |
| Sewing Machine Timing belt |
In internal combustion engines, timing belts work to deliver synchronized rotational motion from the engine crankshaft to the engine camshaft.
This results in a synchronized motion between the engine piston and inlet & outlet valve.
Another relatively new but interesting application of the timing belt is a 3D printer. 3D Printer uses a timing belt to transfer motion from its stepper motor to its building platform and nozzle or hot end.
Other than this there are hundreds of different timing belt applications like
- Small CNC machines
- Small synchronized conveyor mechanism
- Treadmill
Types of Timing Belts
Based on the application there are several types of timing belts. These types of the timing belt can be arranged into the following patterns- Imperial system timing belt
- Metric system timing belt
Note: Pitch is the linear distance between a point on one tooth and the same point on the next consecutive teeth.
Next in each system of measurement, a timing belt can have several teeth profiles including
- Trapezoidal
- Curvilinear
In the curvilinear tooth profile, the timing belt teeth work smoothly as belt teeth move more deeply into pulley teeth. This enables high power and torque transmission between rotational motion input and output.
Some other very specific timing belt profiles help to deliver synchronized rotational motion in some very dedicated applications. These timing belt profiles include
- Standard Trapezoidal tooth profile
- High Torque Drive Profile HTD
- High Power Drive Profile STD
- High Power Drive Profile RPP
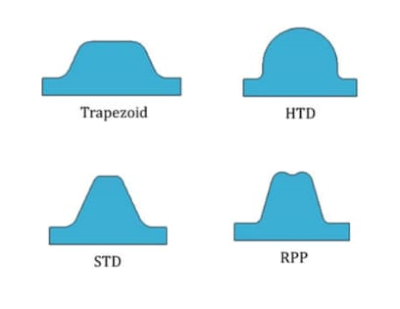 |
| timing belt profiles |
Advantages and Disadvantages of a Timing Belt
Advantages Of a Timing Belt
- A Timing belt is much quieter than a timing gear and timing chain. They produce zero to very low levels of noise.
- It is a cost-effective solution for synchronized power and rotational motion transfer.
- It takes a lot less effort and costs during maintenance and replacement. They are very easy to maintain and replace as compared to timing chains and gear.
- It is a very lightweight as compared to a gear and timing chain. So it does not put extra weight on the engine of any machine.
Disadvantages Of a Timing Belt
- A timing belt has a shorter life span as compared to a timing chain and timing gear. So they involve much more replacement work as compared to other methods.
- It can easily be affected by dirt and engine oil. So they need regular maintenance and inspection. This adds cost and time against them.
- It can only work for small loads as compared to timing gear and timing chain. They are recommended for small engines only.
- It has much greater chances of stretching over time as compared to timing gear and timing chain. This can affect engine synchronization.

No comments:
Post a Comment